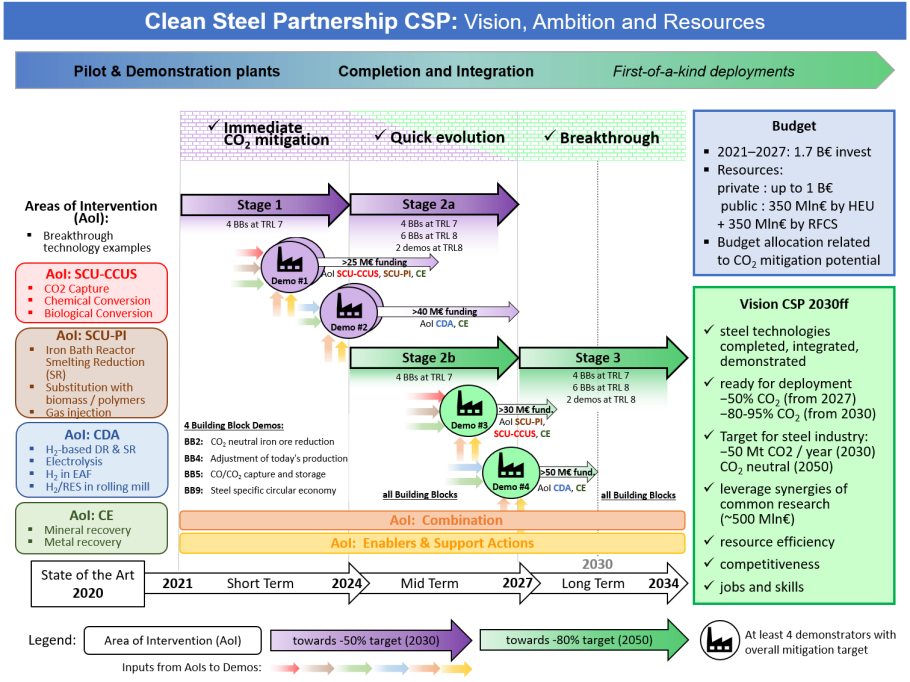
The Clean Steel Partnership (CSP) aims to decarbonise the European steel sector and transform it into a vital, sustainable and circular industry. It tackles two major challenges: fighting against climate change and ensuring sustainable growth for the EU. The CSP is a European co-programmed public-private Partnership established between ESTEP – as the private entity – and the European Commission in the context of Cluster 4 (Digital, Industry and Space) of the Horizon Europe funding programme and the Research Fund for Coal and Steel.